2023 OS LAB2课下共有10个题目,分别是:
- Exercise-完成
mips_detect_memory函数 - Exercise-完成
queue.h - Exercise-完成
page_init函数 - Exercise-完成
page_alloc函数 - Exercise-完成
page_free函数 - Exercise-完成
pgdir_walk函数 - Exercise-完成
page_insert函数 - Exercise-完成
tlb_out函数 - Exercise-完成
_do_tlb_refill函数 - Exercise-完成
do_tlb_refill函数
下面会重点分析第六个练习
Exercise 2.6 完成 pgdir_walk 函数
pgdir_walk,顾名思义,可以理解为walk padir,也就是使得页面目录移动。
该函数的作用是:给定一个虚拟地址,在给定的页目录中查找这个虚拟地址对应的物理地址,如果存在这一虚拟地址对应的页表项,则返回这一页表项的地址;如果不存在这一虚拟地址对应的页表项(不存在这一虚拟地址对应的二级页表、即这一虚拟地址对应的页目录项为空或无效),则根据传入的参数进行创建二级页表,或返回空指针。
但是这个解释过于抽象,实在看不懂。于是我搬来了课程组给出的图,结合实验代码尝试理解:
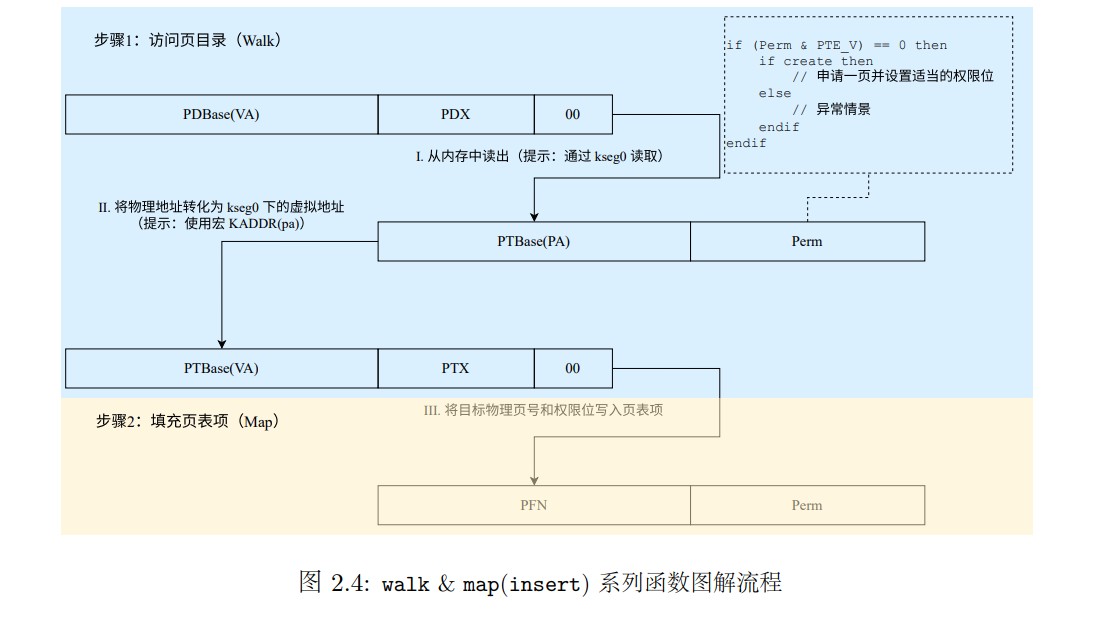
我们的最终目标是什么?获取一个页表项的地址。怎么获取它?我们注意到我们的MOS操作系统是使用两级页表的,我们手中的虚地址,是由页目录索引、页表索引以及页表项内的偏移量组成的。为了获取最终的页表项,我们需要先由页目录基地址+页目录索引得到对应的页表,再由页表+页表索引得到最终的页表项。好比我们想找到一本书的某一页,我们有这本书的目录、章节相对于目录的位置,这一页在章节中的位置。我们可以先查到这一页在哪一章,再查到这一页在本章的哪一节。
现在我们大致懂得了这个过程的基本原理,我们不妨抽象一下这个结构,使之适用于更多级的页表结构。假设我们手中有第级目录的地址和第级子目录相对与级目录的偏移量(或者索引,位置),我们通过就可以得到第子目录的地址,这个过程可以递归进行。
解决了这个问题,我们就可以很快写出代码了:
static int pgdir_walk(Pde *pgdir, u_long va, int create, Pte **ppte) {
Pde *pgdir_entryp;
struct Page *pp;
/* Step 1: Get the corresponding page directory entry. */
/* Exercise 2.6: Your code here. (1/3) */
pgdir_entryp = pgdir + PDX(va); //get 31-22 address of va //PDBase + PDX + 00_2 | co expression
/* Step 2: If the corresponding page table is not existent (valid) and parameter `create`
* is set, create one. Set the permission bits 'PTE_D | PTE_V' for this new page in the
* page directory.
* If failed to allocate a new page (out of memory), return the error. */
/* Exercise 2.6: Your code here. (2/3) */
if ( (*pgdir_entryp & PTE_V) == 0)
{
if (create)
{
if ( page_alloc(&pp) != 0)
{
return -E_NO_MEM;
}
*pgdir_entryp = page2pa(pp);
*pgdir_entryp = *pgdir_entryp | PTE_D | PTE_V;
pp->pp_ref++;
}
else
{
*ppte = NULL;
return 0; //directly return
}
}
/* Step 3: Assign the kernel virtual address of the page table entry to '*ppte'. */
/* Exercise 2.6: Your code here. (3/3) */
*ppte = (Pte *)KADDR(PTE_ADDR(*pgdir_entryp)) + PTX(va);
return 0;
}
需要注意的点:
- 这里可能会在页目录表项无效且
create为真时,使用page_alloc创建一个页表,此时应维护申请得到的物理页的 pp_ref 字段。 记得实时更新pp_ref字段,无论是创建页表项或者使用页表项,都要考虑是否需要更新pp_ref。 *ppte = (Pte *)KADDR(PTE_ADDR(*pgdir_entryp)) + PTX(va)这个语句不是特别好像,似乎应该这么写:*ppte = (Pte *)KADDR(*pgdir_entryp) + PTX(va),但是这样就kernel panic了,为什么呢?这是因为*pgdir_entryp为页表对应的地址,而这个地址低12位是不为零的,会作为一些功能位,如果不清零的直接加上PTX(va),就会将功能位也参与运算,导致地址计算错误。所以要使用低位清零函数KADDR(*pgdir_entryp)将低12位清零,以保证正确性。

